In the ever-evolving Web3 and blockchain technology space, data protection and security have become concerns for users and developers alike. Blockchain networks promise decentralized and trustless systems but also introduce unique challenges and potential vulnerabilities.
This article will explore various problems users face in the blockchain ecosystem, such as key management, transaction privacy, off-chain communication, access control, smart contract vulnerabilities, and network attacks. We will also discuss potential solutions and best practices to ensure a secure and private experience for everyone in this emerging space.
Key management complicates end-user security
Key management in the blockchain ecosystem can be challenging, particularly for non-technical users. Private keys are the primary means of authentication and access to digital assets, and their security is paramount. Users often store keys on PCs or smartphones, which are vulnerable to theft or compromise, and they must securely manage seed phrases for backup recovery.

Various solutions have emerged to address these concerns:
-
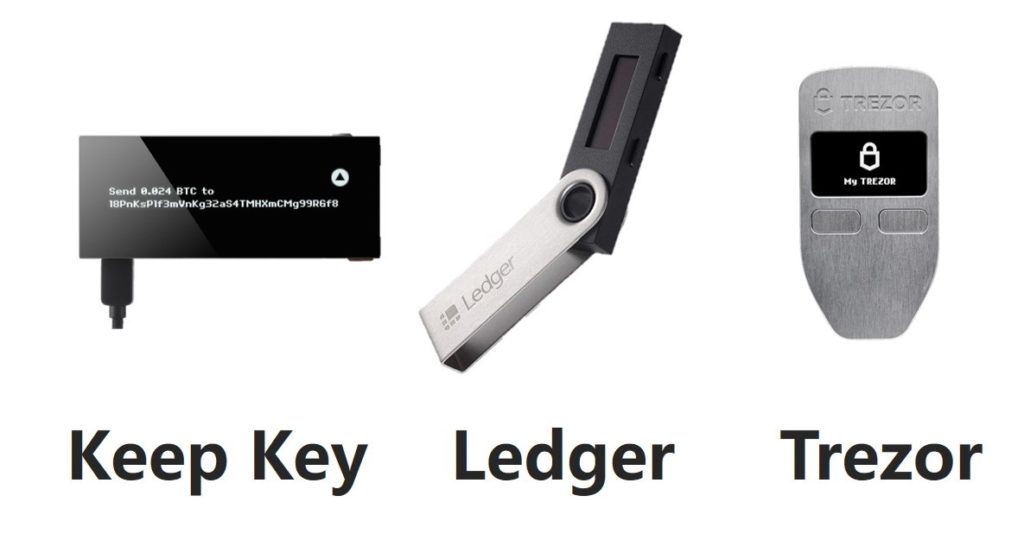
Hardware wallets like Ledger and Trezor store private keys on secure, offline devices. The private key never leaves the wallet, reducing the risk of theft or compromise.
-
Smart contract wallets, like Argent, offer alternative authentication methods to private keys or seed phrases. They use smart contracts to enhance security and simplify access management.
-
Multi-party computation wallets, such as Web3Auth and Lit PKP, utilise advanced cryptographic techniques like threshold cryptography. These wallets ensure the private key is never in one piece at the user's device and allow other authentication methods for added security.
Public transactions are a privacy concern
Blockchain networks, especially public and permissionless ones, offer transparency but at the cost of user privacy. Transactions and account balances are visible to everyone, revealing sensitive financial information about users.
Several solutions address these concerns:
-
Anonymized blockchain networks, like Zcash and Monero, use zero-knowledge proofs and dummy addresses to obfuscate transaction details and protect user privacy.
-
Crypto mixers, such as Tornado Cash Nova and YoMix.IO, split and submit transactions at different times using indirect addresses, making it harder to trace them to individual users.
-
Layer-2 Privacy Protocols, like Aztec Protocol and ZK-Rollups, add a privacy layer to existing blockchains (e.g., Ethereum) using cryptographic techniques, enabling private transactions without requiring separate blockchains or mixers.
Leveraging these solutions, users can maintain the blockchain's security and decentralization benefits while preserving their privacy, ensuring a confidential and secure experience in the digital asset ecosystem.
Off-chain communication is often centralized
Blockchain networks offer decentralization, but their expensive and slow nature makes them unsuitable for day-to-day interactions. Projects often rely on cheaper centralized messaging and data storage services, compromising the decentralized ethos.
Various solutions try to solve this problem:
-
Mixnets like HOPR work alongside blockchain networks, encrypting traffic by default and operating on a peer-to-peer architecture for secure, private off-chain communication.
-
Storage networks like Storj provide encrypted and distributed data storage, enabling users to store and share data without relying on centralized services.
-
Decentralized messaging platforms like Status and Matrix offer secure communication channels built on decentralized infrastructure, using end-to-end encryption and peer-to-peer protocols.
These solutions allow users to enjoy the benefits of blockchain technology while maintaining efficient, cost-effective, and decentralized off-chain communication, upholding the core principles of decentralization and reducing reliance on centralized intermediaries.
Access control for decentralized data is hard to maintain
In theory, blockchain users can use their keys to encrypt any data they like. However, implementing a maintainable and user-friendly access control system for decentralized data takes more work. Users need a secure and scalable method to manage access rights and permissions in a decentralized environment.
Solutions like Lit Protocol utilise blockchain keys or addresses for authentication while encrypting data with distributed key pairs. This approach simplifies access control management and enhances security by separating authentication from data encryption.
With solutions like this, users can manage access control for decentralized data more effectively, maintaining blockchain technology's security and privacy benefits while ensuring a user-friendly experience. This approach helps build robust decentralized applications that securely manage sensitive data and access permissions.
Smart contract vulnerabilities are a constant thread
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with the terms directly written into code. They enable trustless transactions on blockchain networks but can also introduce security risks due to vulnerabilities in the code. Malicious actors can exploit these vulnerabilities, leading to theft or loss of funds, unauthorised access, or data manipulation.
Several solutions have emerged to address smart contract vulnerabilities:
-
Regular audits by specialised blockchain security firms, like ConsenSys Diligence and Trail of Bits, help identify and fix potential vulnerabilities before deploying smart contracts on the network.
-
Developers can offer financial incentives to ethical hackers and the wider community to uncover and report vulnerabilities in their smart contracts, allowing for proactive identification and resolution of security issues.
-
Solutions like Nexus Mutual provide insurance coverage for smart contract vulnerabilities, compensating users for potential losses due to exploits or hacks.
By employing these strategies, developers can minimise the risks associated with smart contract vulnerabilities, ensuring a more secure and reliable user experience within the blockchain ecosystem.
Network and consensus attacks can destabilise the ecosystem
Blockchain networks rely on consensus algorithms to validate transactions and maintain the integrity of the distributed ledger. However, these networks can be vulnerable to attacks that disrupt consensus or manipulate the network's functionality. Examples of such attacks include 51% attacks, Sybil attacks, and Eclipse attacks.
Different strategies mitigate the risk of network and consensus attacks:
-
Projects like Algorand and Cardano, use alternative consensus algorithms like Proof of Stake (PoS) or Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) to minimise the risk of attacks and increase network security.
-
Enhancing P2P network security with reputation systems, secure node discovery, and advanced cryptographic techniques can help protect against Sybil and Eclipse attacks.
-
Implementing layer-2 scaling solutions, like plasma, optimistic rollups, or zero knowledge rollups , can reduce the attack surface by offloading a portion of the network's operations to secure side-chains or off-chain mechanisms.
-
Interoperability solutions like Polkadot and Cosmos can create a more resilient ecosystem by enabling communication between multiple blockchains, which helps distribute risk and reduce the impact of an attack on a single network.
These strategies allow developers to build more robust and secure blockchain networks resistant to network and consensus attacks, ensuring a safer and more reliable experience for users.
Conclusion
While blockchain technology has revolutionised data protection and security, it also presents unique challenges. Addressing issues such as key management, transaction visibility, off-chain communication centralization, decentralized data access control, smart contract vulnerabilities, and network and consensus attacks is critical to ensure the safety of your users.
Fortunately, many innovative solutions and strategies have emerged to tackle these challenges. By adopting and refining these solutions, we can continue to build a more secure, private, and user-friendly blockchain ecosystem that upholds the core principles of decentralization and empowers users to harness the full potential of this transformative technology.
Akava would love to help your organization adapt, evolve and innovate your modernization initiatives. If you’re looking to discuss, strategize or implement any of these processes, reach out to [email protected] and reference this post.